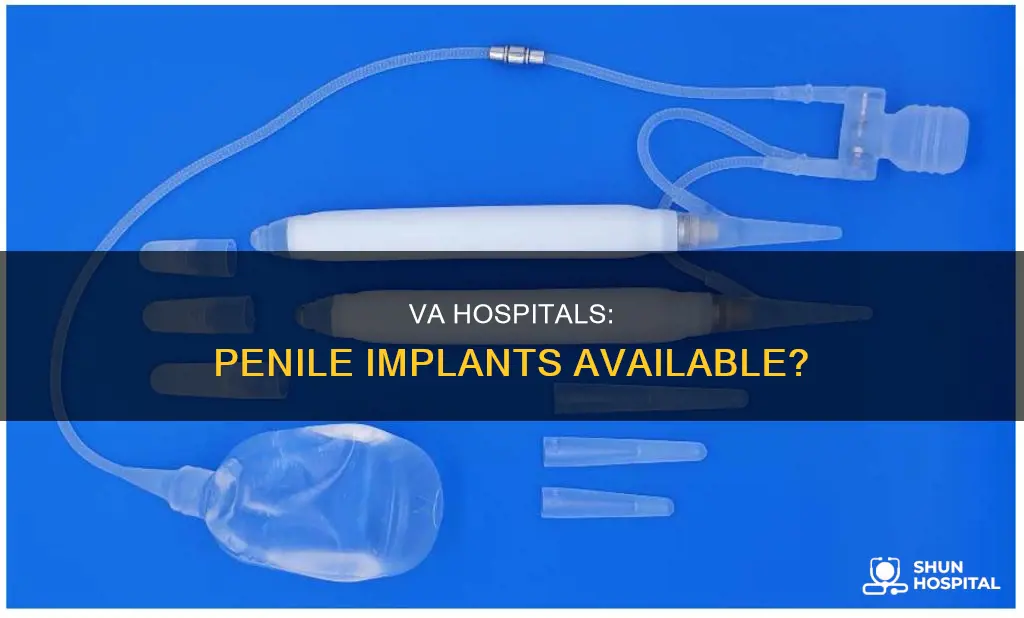
Penile implants are a treatment option for men suffering from impotence or erectile dysfunction. The procedure involves placing a device inside the body to help the patient achieve an erection. Inflatable Penile Prosthesis (IPP) is one type of penile implant that consists of a cylinder or two in the penis, a pump in the scrotum, and a saline reservoir in the lower abdomen. While penile implants are typically considered a long-term solution with high patient satisfaction rates, there are risks associated with the surgery, including infection and mechanical failure. In the context of VA hospitals, there is evidence of veterans undergoing penile implant procedures, including at the Jackson VA Medical Center, indicating that penile implants may be offered as a treatment option within the VA healthcare system.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What | Penile Implant |
| Who | Veterans |
| Where | VA Hospital, Jackson VA Medical Center, New Orleans VA Medical Center |
| Why | To treat erectile dysfunction, Peyronie’s disease, impotence |
| How | Surgical procedure with a 3% risk of infection |
| Implant Details | Inflatable Penile Prosthesis (IPP) with a cylinder or two in the penis, a pump in the scrotum, and a saline reservoir in the lower abdomen |
| Recovery | 4-6 weeks |
| Patient Satisfaction | 93.8% |
What You'll Learn

Inflatable Penile Prosthesis (IPP)
IPP surgery is a common procedure, with over 63,000 implants performed worldwide between 2005 and 2012. It offers a discrete solution, emulating the look and performance of a natural erection. The recovery period is typically four to six weeks, during which patients should follow their physician's recommendations for a successful outcome.
While IPP provides high patient satisfaction, with 93.8% reporting moderate to complete satisfaction, it is important to carefully consider this option. Once implanted, natural erections are eliminated, and medications will no longer be effective. Additionally, there is a risk of mechanical failure, with implants lasting an average of 10 to 15 years.
IPP implantation involves surgical exposure of the corpora, corporal dilatation, cylinder placement, tubing positioning, and RTE use. Over time, friction between components can lead to cylinder erosion and leakage, known as "input tubing wear." A more proximal corporotomy incision may help resolve these issues and reduce the need for RTEs.
Postoperative care includes monitoring for infection signs, such as swelling, pain, and discharge from the wound site. While localized infections can be treated with antibiotics, prosthesis removal may be necessary if antibiotic therapy is ineffective.
Heart Attack Treatment: Hospital Procedures and Protocols
You may want to see also

Surgical procedure and recovery
Penile implants are surgical solutions for erectile dysfunction. The procedure involves inserting an implant—either malleable or inflatable—into the penis to facilitate an erection. The implant is custom-fitted to the patient's anatomy.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes incisions in the penis and, if opting for an inflatable implant, the abdomen. The implant is then inserted, and the incisions are closed with dissolvable stitches. Small silicone tubes may also be stitched into the incision sites to drain blood and fluid. A bandage is then placed over the wound. The surgery typically takes one to two hours, and the patient is usually conscious.
After surgery, the patient is moved to a recovery room, where healthcare providers monitor their overall health. The patient can usually go home the same day, but they will need to arrange transport as they will still be groggy from the anaesthesia. The patient will likely experience pain, swelling, and discomfort for up to a week after the surgery, and tenderness for up to six weeks. Their care team may prescribe antibiotics and pain medication. Stitches will be dissolvable and do not need to be removed. Patients will also be instructed on postoperative wound care, including monitoring for signs of infection.
The patient will need to abstain from sex for a few weeks, and a follow-up appointment will be scheduled for four to six weeks after the surgery, once the swelling has decreased. At this appointment, the patient will be instructed on how to use their implant.
While the surgery is considered safe, there are some uncommon risks, including uncontrolled bleeding, damage to the urethra, infection, excessive scar tissue, erosion, pump or reservoir displacement, mechanical failure, and decreased blood flow to the head of the penis.
Exploring the Hokkaido Hospital in Hitman: Fact or Fiction?
You may want to see also

Patient satisfaction
While individual results may vary, penile implants have been shown to have high patient satisfaction rates. One source reports that 93.8% of patients were moderately or completely satisfied with their penile implants, which is significantly higher than the satisfaction levels reported for alternative treatments such as Viagra (51.6%) or injection therapy (40.9%).
The high satisfaction rates associated with penile implants can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the implants are custom-fitted to each patient's anatomy, ensuring a natural look and performance. Secondly, the implants offer a long-term solution to erectile dysfunction, with a typical recovery period of 4 to 6 weeks. During this recovery period, patients should closely follow their physician's recommendations to ensure optimal outcomes.
Additionally, penile implants provide a discrete solution, as they are completely placed inside the body and are designed to emulate the look and performance of a natural erection. This means that no one will be able to tell that an individual has an implant unless they choose to disclose it.
It is important to note that penile implants may not be suitable for everyone. Patients should carefully consider their medical condition, lifestyle, personal preferences, and cost before opting for this treatment. Consulting a physician is crucial to understanding the risks and benefits of penile implants and determining if this treatment aligns with an individual's specific needs and circumstances.
EMTALA and Private Psychiatric Hospitals: Who's Covered?
You may want to see also

Implant removal
Penile implants are used to treat erectile dysfunction and sometimes Peyronie's disease. While the risk of infection is low (3%), implant removal may be necessary if an infection develops. Antibiotics are usually prescribed, and a closed suction drain may be left in the penis or scrotum temporarily.
In some cases, the implant may need to be removed without replacement. This is usually due to infection or skin erosion, and it is important to understand that most men will not be able to obtain erections after the implant is removed without a replacement.
One case study describes a veteran who underwent a penile implant procedure at the Jackson VA Medical Center. The implant became infected, and the veteran went to a private hospital where the implant was removed, and antibiotics were prescribed.
The removal of a penile implant can be challenging, especially for non-specialists. The classic penoscrotal incision can increase the risk of complications and make future re-implantation more difficult. However, alternative surgical techniques have been developed that avoid this approach and reduce the risk of urethral damage and fibrosis.
The removal procedure typically involves making multiple incisions directly over each component of the implant for their extraction. Incisions are made on both sides of the ventral base of the penis, an inguinal incision, and a scrotal incision.
After the procedure, patients may experience some pain for 1-2 weeks. They are usually advised to apply a compressive dressing for the first 24-48 hours and can typically return to work within 2 weeks. Showering is permitted the day after the procedure, but swimming in a public pool or the beach should be avoided until the incision has completely healed (usually 3-4 weeks).
Helen's Hospitality: Aiding Odysseus
You may want to see also

Treatment options
Penile implants are a treatment option for men suffering from impotence or erectile dysfunction. The implant is a device placed into the body to help men get an erection. The Inflatable Penile Prosthesis (IPP) is one such implant, consisting of a cylinder or two in the penis, a pump placed inside the scrotum, and a reservoir of saline in the lower abdomen. Squeezing the pump moves the saline into the cylinders, creating a rigid and natural-feeling erection. The erection can be maintained as long as desired and deflated when finished.
The implant procedure is surgical and, as such, carries a risk of infection, typically very low at around 3%. There is also a risk of mechanical failure, with implants lasting on average 10-15 years. The implant eliminates the possibility of a natural erection, and considerations for choosing this treatment option include medical condition, lifestyle, personal preference, and cost. It is a long-term solution and, according to one source, 93.8% of patients were moderately or completely satisfied with their penile implant choice, compared to lower satisfaction levels for Viagra or injection therapy.
Before opting for an implant, it is important to discuss treatment options with a physician to understand the risks and benefits and determine if an implant is the right choice. This includes considering whether one can still have satisfactory erections without an implant. The recovery period after the procedure is typically around four to six weeks, during which the patient should follow the physician's recommendations for care.
Insurance coverage is an important factor when considering penile implants. Most commercial insurances, Medicare, and VA insurance may cover penile implants when deemed medically necessary. However, each insurance company has different standards for determining coverage. It is crucial to contact the insurance company to understand their specific criteria and whether penile implantation is excluded from the plan. Additionally, the final cost of the procedure may vary depending on timing and other incurred medical costs.
Effective Ways to Remove Hospital Tape Residue
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A penile implant is a device that is placed into a man’s body and is designed to help him get an erection. It consists of a cylinder or two in the penis, a pump placed inside the scrotum, and a reservoir of saline in the lower abdomen.
Yes, VA insurance may cover a penile implant when it is considered medically necessary. However, it is important to note that each insurance company will have different standards to determine coverage.
The process typically involves an initial consultation with a physician to determine if a penile implant is the right choice for you. If it is deemed medically necessary, the implant procedure will be scheduled. After the surgery, there is a four-to-six-week recovery period before the implant can be used. During this time, the patient should follow the recommendations provided by their physician to ensure optimal recovery.







